Introduction
Guards wrap parts of your code and guard it from overload, ensuring high-priority requests are always served, and slowing or dropping lower priority requests if needed. Guard quotas can be changed in real time if needed (for instance, if you lose a database replica or cloud region and can only service half of your usual traffic). Good uses for guards are wrapping outgoing requests to resource constrained services like ChatGPT, Postgres, MySQL or Redis, to ensure they are not overloaded and prevent abuse. You can also use guards as a top-level middleware to guard a service from overload by incoming requests. This can be useful to protect a service from large auto-scaling bills, or DDOS-ing Yourself bugs.
Creating Guards
- From the left hand side menu, select "Guards".
- Click on

- Add a unique Name.
- Select the correct Traffic Type and click Save.
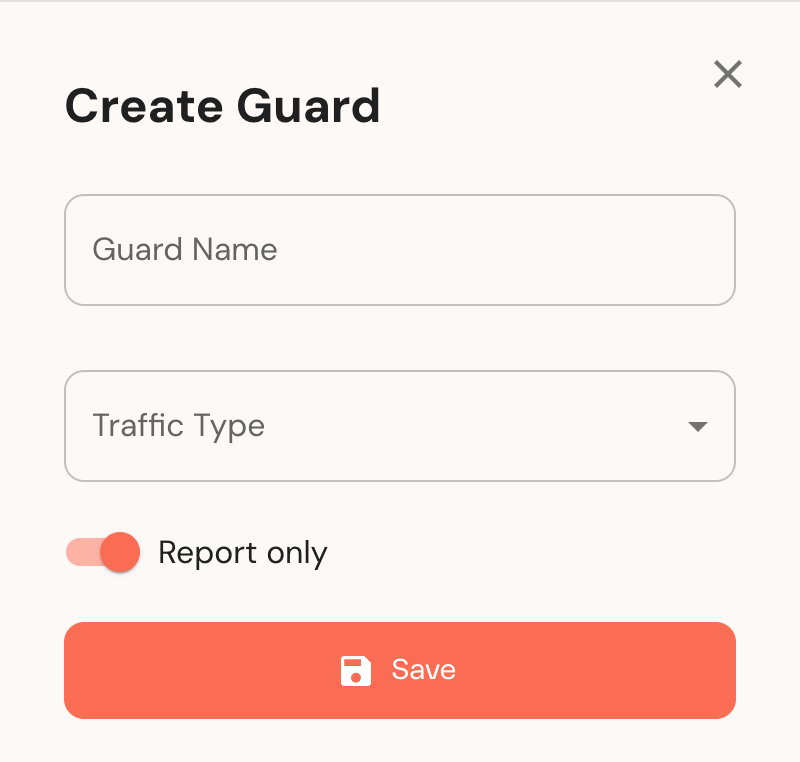
- You'll be redirected to your Guard's details page.
Configuring Guards
Quota Configurations
Guard behavior is configured using the Quota Configuration. By default, your guard was created with an empty traffic configuration that you can modify to meet your needs. There are many quota configuration options - read the configuration section for more information
Optional Configurations
Guards have two optional configurations that are for your records:
- Traffic Type
- Guarded Service - the service that the guard guards (if this is an 'outbound' traffic guard, it will not be the same as the service the guard is in.)